Over 10 years after the first application for a spot Bitcoin ETF was filed, the SEC finally approved the launch of BTC spot exchange traded funds on January 11, 2024. Due to this significant news for the industry, in our new piece we will explore what ETFs are, how they work and why traders invest into them.
What is an ETF (exchange traded fund)?
The idea of investing in indices dates back quite a long time ago: from time to time, trusts or closed-end funds were founded in order to give investors the opportunity to invest in a certain type of assets.
The first fund based on the idea of passive investing was launched in 1976 by John Bogle, founder of The Vanguard Group. But the creation of ETFs in the modern concept occurred decades later, and in 1993 State Street Global Investors launched the S&P 500 Trust ETF, which is still one of the most actively traded ETFs today. And as of January 2024, there are already more than 600 different ETF issuers.
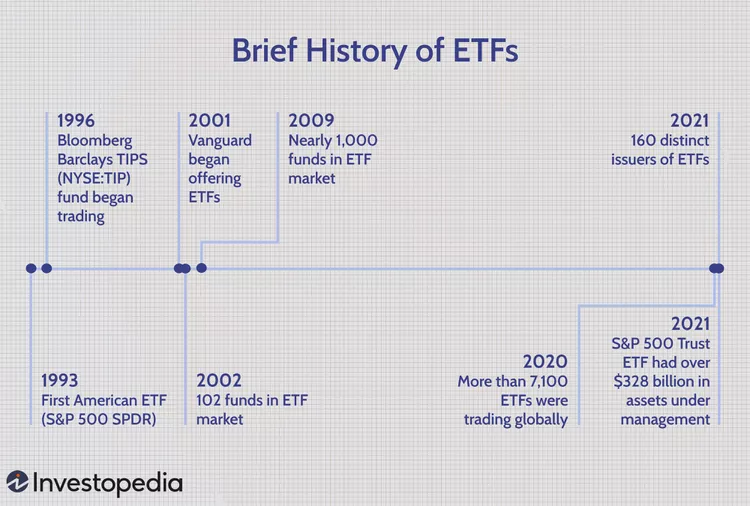
So what is an ETF (exchange traded fund)? Broadly speaking, it is an investment instrument. More precisely, an ETF can be defined as an exchange traded investment fund that holds a collection of securities based on a chosen index (e.g. Dow Jones, S&P 500 or NASDAQ), sector, commodity or other asset.
How exchange-traded funds work
In order to better understand what an ETF is and why it is favored by investors, we suggest understanding how this kind of fund works.
- Fund Creation. A financial institution decides to create an ETF.
- Regulatory approval. Before an ETF is introduced to the public, its company must receive approval from the relevant authorities, such as the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC).
- Acquisition of assets. The Fund purchases a number of assets for its portfolio, for example, securities of companies in a certain industry.
- Issuing shares of the fund. The fund then issues its own shares, which will then be traded on an exchange. Within one ETF, there can be hundreds of stocks from different industries, or it can be tied to one specific industry, sector or commodity.
- Investors purchase shares of the fund. Then, the reason why the fund was created takes place – investors get an opportunity to buy ETF shares. This allows them to invest, for example, in all securities included in the index on the basis of which a particular fund is assembled. It is objective, it is more convenient than an independently collected portfolio.
Which types of ETFs are there?
ETFs as a relatively safe investment instrument are widely spread in the international financial market. Thus, as of 2020, the number of exchange-traded funds in the world was more than 7,600. Therefore, we would like to bring order to this diversity and first divide them into traditional and cryptocurrency ETFs. In our article, we will not go into detail about the traditional ones that offer access to stocks, bonds and commodities, and will focus on crypto funds.
From the category name, it is clear that these funds are tied to the price performance of one or more cryptocurrencies. As in the case of traditional ones, the shares of cryptocurrency ETFs are also traded on exchanges.
There are many different variations of cryptocurrency ETFs that can be picked according to an investor’s preferences and risk tolerance. In general, they can be categorized into single-asset, multi-asset and sector ETFs, each of which can be divided into spot and futures.
- Single-Asset Cryptocurrency ETFs
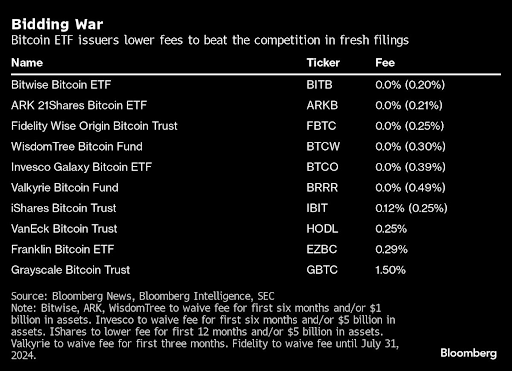
Single-asset cryptocurrency ETFs are focused on one type of cryptocurrency, such as Bitcoin or Ethereum. In the context of bitcoin, ETFs give investors the opportunity to capitalize on the movement of its price without holding the cryptocurrency itself. Instead of dealing with exchanges and wallets themselves, an investor can buy shares through simple brokerage accounts. Examples of such a fund include BlackRock’s recently approved iShares Bitcoin Trust, Fidelity’s Wise Origin Bitcoin Trust, VanEck Bitcoin Trust, WisdomTree Bitcoin Trust, the Invesco Galaxy Bitcoin ETF, and others.
- Multi-asset cryptocurrency ETFs
A solution for investors looking for diversification in the cryptocurrency space. Such funds invest in a variety of digital assets, spreading risk across different cryptocurrencies. An example of such a fund is the CI Galaxy Multi-Crypto ETF. Such a diversified approach helps mitigate the impact of underperformance of a single asset on the entire portfolio.
- Sector ETFs
These ETFs concentrate on companies in the crypto industry, rather than cryptocurrencies specifically. These companies can include centralized crypto exchanges, bitcoin mining operators and technology companies that produce cryptocurrencies or blockchain-based solutions. As an example, consider the Bitwise ETF, which tracks an index of leading companies in the industry.
Within the categories described, cryptocurrency ETFs can be distinguished based on whether they operate in the spot or futures market. Spot ones directly hold the underlying cryptocurrency, while futures ones hold futures contracts that forecast the price at a future date.
How to invest in crypto ETFs
One of the advantages of cryptocurrency ETFs is that you can invest in them just like you can invest in traditional ETFs. Once you determine which ETF you want to invest in, you can use your brokerage account to place an order to buy shares.
Let’s look at how to invest in ETF shares with an example of the recently approved ARK 21Shares.
- An investor can purchase shares of the fund on the broker’s website. The company’s ticker symbol is ARKB. On its website you can find the list of supported platforms.
- Through a financial advisor.
- The fund also provides shares for financial professionals and institutions.
Advantages and disadvantages of crypto ETFs
Now when we have figured out the basic concepts and principles of ETFs, it is time to sum up the advantages and disadvantages of these investment assets.
Pros of crypto ETFs
Diversification. involves adding a unique asset class to a portfolio to enhance its diversification.
Simplicity. For most investors, buying ETF shares is much easier than buying and holding cryptocurrency directly.
Safety. An ETF does not require you to own cryptocurrency, store keys securely, or move them between different types of storages, which in this context may be more convenient and safer for you.
Cons of ETFs
Commission. When you invest in ETFs, you pay a brokerage commission, if any, as well as the fund’s yearly expense ratio to cover operating expenses.
Dependence on the fund manager’s strategy. A disadvantage common to all ETFs is that you give up some control. You rely on the strategies of the fund manager, whose qualifications play an important role.
Lack of 24-hour trading. Generally, you can only buy and sell ETFs during regular stock market hours. Cryptocurrency exchanges or crypto bots, which automate your trading, operate 24 hours a day.
How the approval of a spot bitcoin ETF affected the market
The launch of exchange-traded funds on January 11 was an important milestone for bitcoin in the cryptocurrency industry. However, its price did not rise as impressively as expected. At the time of writing, January 19, despite reaching a two-year high of $49,051 on January 11, the major cryptocurrency is trading below the $41,000 level.
According to the analytical company CryptoQuant, the so-called “buy rumors, sell facts” phenomenon has occurred. This means that when the price of an asset grows in anticipation of positive news, the growth does not always follow the event. That is, the anticipation of spot ETF approval led to a rise in the price of bictoin even before the ETF was approved, so a correction is more likely to occur after the approval. In addition, CryptoQuant analysts predicted that the bitcoin price could fall to $32,000 after the ETF was approved.
Bitcoin’s price surge is expected in the long term – many investors believe it will begin to increase later this year, and the effect of ETF approval will consolidate after the highly anticipated halving in April 2024.
The emergence of spot bitcoin ETFs marked an important milestone in cryptocurrency investing, offering a regulated and simplified way to access bitcoin price movements. By potentially increasing market liquidity and attracting more institutional participants, ETFs could play a key role in stabilizing and driving bitcoin adoption.
FAQ
What is an ETF?
ETF (exchange traded fund) is an investment instrument. It can be defined as an exchange traded investment fund that holds a collection of securities based on a chosen index (e.g. Dow Jones, S&P 500 or NASDAQ), sector, commodity or other asset.
How do I invest in an ETF?
You can invest in them just like you can invest in traditional ETFs. Once you determine which ETF you want to invest in, you can use your brokerage account to place an order to buy shares.
