You’ve probably heard that Ethereum is the most popular blockchain when it comes to creating smart contracts and dapps, due to its flexibility, development-friendly interface, and reliability. But there are many other blockchain networks that can easily compete with Ethereum, and Binance Smart Chain is one of them. So let’s find out what BSC is and how it works!
The roots of Binance Smart Chain
The history of Binance Smart Chain, or simply BSC, is inextricably linked to Binance Coin (BNB), Binance Exchange, and, of course, its relative, Binance Chain.
In 2017, when the Binance exchange was established, the Binance coin (BNB) was also introduced to the general public, and it first operated as an ERC-20 token. All these events marked the beginning of the construction of the Binance Smart Chain network.
Back then, BNB was first operating on the Ethereum blockchain. However, in 2019, the BNB developing team created a streamlined blockchain called Binance Chain (BC), which makes use of the Tendermint byzantine-fault-tolerant (BFT) consensus mechanism. After the introduction of Binance Chain, BNB was migrated from the Ethereum blockchain to become the native cryptocurrency on Binance Chain.
Utilizing a distributed consensus method, the Binance Chain was designed to provide blazing-fast transaction speed, making it ideal for a quick yet secure exchange of digital assets. Even though Binance Chain quickly became popular among traders, its technology still lacked the functional capability for smart contract execution. Thus, to satisfy the needs for smart contract capabilities, Binance Smart Chain was developed as a parallel blockchain.
In September 2020, around one and a half years after the debut of its predecessor BC, Binance Smart Chain (BSC) went live. Despite having the option, Binance chose to introduce a new blockchain following the Binance Chain instead of improving it. The reason why Binance decided to create a parallel blockchain is that adding smart capabilities to the BC blockchain would have slowed network speed, plus it would have reduced network efficiency.
Even though Binance Smart Chain is perceived as a unique blockchain with its own technologies and capabilities, it’s interesting to note that Binance developed its Binance Smart Chain by forking the Go Ethereum (Geth) client but made a few modifications to set it apart from Ethereum. In contrast to Ethereum’s back-then present Proof of Work (PoW) consensus protocol, they chose a Proof of Staked Authority (PoSA) consensus mechanism. PoSA allows for short block times and cheap transactions.
Still, even though Binance Chain and Binance Smart Chain are not quite the same, Binance decided to unite them both under one name — BNB chain — to make their connection to Binance token BNB look more obvious. Moreover, the BNB chain should now be read as the “Build and Build” chain.
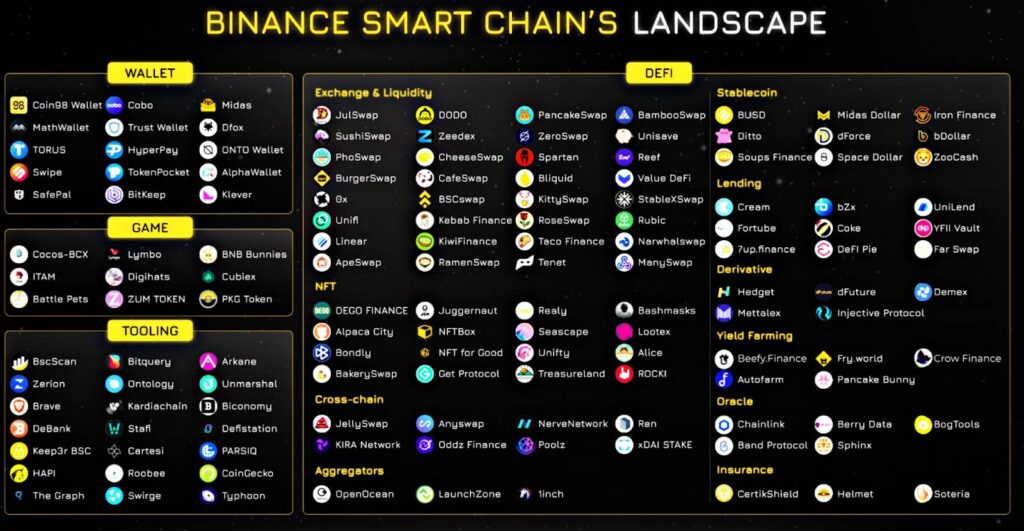
BSC landscape
The BNB chain can easily compete with Ethereum in terms of the number of developed projects. There is a high chance that you’ve definitely heard about these DApps, but probably never knew that they are built on BSC.
Pancake Swap, for example, is one of the largest and most well-known decentralized exchanges, and it is built on Binance Smart Chain. Pancake Swap started its journey as a DEX, but nowadays it includes an NFT marketplace, farming, staking, and even a lottery, in which you can win 50% of the entire lottery pool, which can vary from day to day (as of 22.09.22, it is equal to around $120K).
Another example is the Venus lending protocol which works as an algorithmic money market, where users can instantly borrow and lend money, since this system does not imply any middlemen. Thanks to Binance Smart Chain support, Venus operates at a high speed and enables almost instantaneous transactions with low transaction fees.
ApolloX is another example of a BSC DApp that gained popularity and attention among crypto enthusiasts. ApolloX is a DeFi platform that combines CEX and DEX, and it focuses on a cryptocurrency derivatives exchange. Low commissions (zero for a maker), large trading volumes, minimal entry threshold, and quick exchange services that are provided free of charge make ApolloX an attractive DeFi app for those traders who look for something new and non-trivial.
There are hundreds of other DApps that are built on BSC, and the above-mentioned ones represent merely a fraction of them all.
BC vs. BSC. How are they different?
Let’s highlight the differences and similarities between BC and BSC to make it easier to comprehend what these two blockchains are about:
Differences:
- Token standards. While BSC tokens must adhere to the BEP-20 standards, BC network tokens are minted in accordance with the BEP-2 issuance standard. BEP2 is a standard for Binance exchange’s native token – BNB – and it was designed primarily to be used on both centralized and decentralized exchanges.
BSC is more flexible, since it has the capability of introducing more token standards when necessary. As an example, the BEP-721 standard was rolled out when the need for issuing NFTs arised.
Additionally, BEP20 has an advantage over BEP2 due to its supporting compatibility with the Ethereum Virtual Machine. On top of that, there is another advantage of BEP20 tokens, which is interoperability, which enables easy conversion of BEP20 tokens to BEP2 tokens. - Functionality. Binance Chain has a restricted set of capabilities and is currently mostly used to host the Binance DEX. The BSC, on the other hand, can be used for deploying smart contracts and hosting dApps.
- Consensus mechanisms. As we’ve already mentioned above, BC utilizes the Tendermint byzantine-fault-tolerant (BFT) consensus mechanism. On the other hand, BSC uses delegated Proof of Staked Authority (PoSA).
The BFT consensus mechanism allows Binance exchange team to solely manage the BC blockchain without involving the community. In turn, PoSA allows other validators to take part in network governance and block validation. Still, Binance nevertheless has control over the BSC blockchain through its role of vetting block validators.
Similarities:
- Speed. Both blockchains support extremely fast block times. For instance, it takes less than a second per block in case of Binance Chain, and as for BSC new blocks are created every three seconds. In contrast, it takes 20 seconds for Cardano blockchain to create a new block, and 10 minutes for Bitcoin blockchain to add a new block.
- Quite centralized. Binance Chain and Binance Smart Chain are both maintained by Binance exchange team. The only difference is that Binance has less control over BSC than it does over BC, but still, all the major updates and maintenance are centralized and provided by Binance, and not the community.
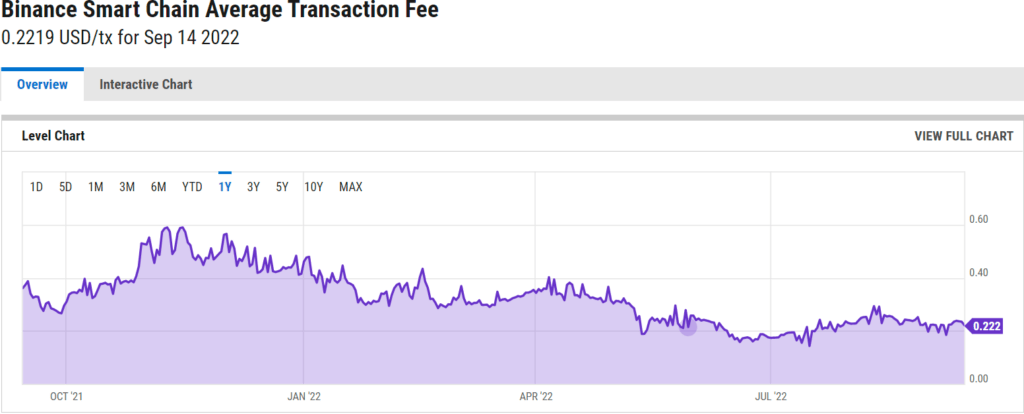
- Fees. Compared to the Bitcoin and Ethereum blockchains, transaction fees on both BC and BSC are considerably lower. Thus, BSC fees rarely go higher than $0.60 per transaction, whilst Ethereum fees can go up to an absurd $200 per transaction.
The BSC design principles
Now that we have clarified the differences between Binance Chain and Binance Smart Chain, let’s take a look at the specific attributes of the latter one.
Standalone blockchain
While it operates in parallel with Binance Chain, Binance Smart Chain is an independent blockchain. Thus, in the event that BC stops working due to malfunctioning, BSC will continue to operate to prevent any kind of service interruption. Moreover, making BC and BSC work separately allowed Binance to introduce new capabilities and functions without overloading its network.
Compatibility with Ethereum platform
The majority of Binance’s technology development was accomplished by using Ethereum source code. Binance made the decision to adapt Ethereum’s robust technology with a few tweaks, most notably the consensus mechanism.
Since Binance forked most of Ethereum’s source code, that made cross-chain interoperability much simpler: native Ethereum dApps can be easily transferred to BSC. Thanks to Ethereum compatibility, developers can migrate DApps, tools, and other ecosystem components to the BSC network without too many difficulties.
Native cross-chain interoperability
Even though BSC is not a layer 2 solution and it operates as a parallel blockchain to BC, there is still cross-chain compatibility between them. That means users can freely swap cryptocurrencies between BC and BSC, such as BEP2 and BEP20 tokens.
Staking and governance
Since BSC utilizes a proof-of-stake (PoSA) consensus protocol, BSC’s native token BNB can be staked, thus allowing users to contribute to network security and allow voting on community governance protocols. Moreover, the PoSA protocol enables better network performance than the classic Proof of Work protocol (e.g., Bitcoin), and also enables faster blocking time and higher transaction capacity.
BSC Proof of Staked Authority Consensus mechanism
The BSC consensus protocol is somewhat non-trivial, as it utilizes both delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS) and Proof of Authority (PoA) mechanisms to achieve consensus within the network and maintain blockchain security.
Proof of stake is a consensus mechanism that uses a competitive validation method to confirm transactions and add new blocks to the blockchain. Delegated PoS works in a similar way, but with a few differences: it includes a voting and delegation mechanism that increases the democratic nature of the process. Users of the network have the right to vote and choose “delegates”, or the block producers, who will validate the next block within the blockchain. Via DPoS, you can vote on delegates by staking your tokens into a pool and linking them to a particular delegate.
In Proof of Authority based networks, blocks and transactions are validated by approved accounts, known as validators. Validators run software, allowing them to put transactions into blocks.
Since the PoA consensus mechanism makes use of the value of identities, block validators stake their reputation rather than currency while validating transactions. As a result, PoA blockchains are secured by the validating nodes that are arbitrarily selected as trustworthy entities. In the case of BSC, Binance is the main entity that runs a strict vetting process of the validators.
Validator quorum
The BSC network relies on a validator quorum when it comes to the matter of security. To put it simply, BSC has 21 validators that are chosen every 24 hours by BNB stakers. Technically, anyone can apply for the position of a validator. However, the validator set only includes individuals who belong to the top 21 highest staked nodes.
In order to secure the network from malicious validators, BSC implements “slashing” logic to penalize Byzantine validators for double-signing (a validator signs two blocks at the same time), instability, or any other negative behavior. To put it simply, slashing refers to the process of taking or “slashing” a fixed amount of a validator’s stake. Such a penalty helps to sustain order and makes validators behave themselves in a righteous manner.
Pros and Cons of Binance Smart Chain
Since its launch in September 2020, the Binance Smart Chain (BSC) has established itself as one of the leading blockchains for dapps and DeFi. Still, BSC has advantages and disadvantages just like any other blockchain network. Let’s highlight some of the most obvious ones:
Pros:
- Low transaction fees. Low transaction fees of less than a dollar due to more or less constant GWEI prices thanks to parallel operating blockchains is one of the biggest advantages of BSC. That is the main reason why BSC is even more popular among play-to-earn game developers than the Ethereum platform.
- Reliability. Binance has established itself as one of the most reputable crypto brands. It is more than simply an exchange; it is a worldwide blockchain corporation that is venturing into a variety of crypto trends, including the creation of its own blockchains. The presence of the exchange is crucial to the PoSA consensus since it verifies each validator on the network, assuring the security and stability of BC and BSC. So, with one of the most well-known crypto exchanges backing its blockchain, you can be sure that its sustainability is in the right hands.
- Smart contracts. Unlike its predecessor Binance Chain, Binance Smart Chain has smart contract functionality, so it is perfectly suited for DApps.
- Ethereum compatibility. DApps built on Ethereum can easily switch to BSC since it is a direct copy of Ethereum source code, plus BSC is compatible with EVM (Ethereum Virtual Machine). The transition is quite simple thanks to the numerous cross-chain bridges offered by Binance and other third parties.
- Cross-chain interoperability. The BSC and Binance are parallel blockchains and they operate concurrently. It implies that users can move their tokens from BSC to Binance chain and vice versa with ease. Moreover, BSC also supports pegged coins from several other blockchains (e.g. Tether, Dogecoin, Polkadot, etc.), thus making the BNB chain extremely flexible.
- Powerful support. In addition to a huge user base, Binance’s support is backed by a sizable amount of technological, human, and financial resources. Just a small example of such support – Binance provided the BSC Accelerator Fund with a $100 million donation from its funds back in October 2020. Through that program, Binance provides liquidity support for the launch of projects based on the BSC ecosystem.
Cons:
- Centralization. Financial, technological, and human support of the BSC comes with centralization. That is, Binance pretty much controls the whole blockchain via the PoSA consensus mechanism, even though that doesn’t affect the regular users. Still, in theory, if something happens on the Binance end, the whole BNB chain would face a major collapse.
- Dependence on Ethereum. BSC is largely dependent on the Ethereum developer community, therefore little innovation occurs within BSC itself, but rather is carried over from Ethereum.
- Security. BSC’s centralized nature makes it vulnerable to 51% attacks, as well as hacking, and system failures, since network validators must be approved by Binance’s internal team.
- Scams. Due to low transaction fees, BSC also makes it more lucrative for scammers than Ethereum. Numerous projects operating on a BSC that pop up by the dozens on a daily basis end up being scams of all sorts, and investors who prefer trading on DEXs over centralized exchanges know this very well.
Final thoughts
Binance Smart Chain offers a great alternative to users who don’t mind centralization and are merely looking for a more affordable, quick, and flexible blockchain than Ethereum, for instance. In addition, BSC lowers the barrier for new traders and investors who would like to make an investment but are not willing to pay too much for transaction fees, or who are looking for more affordable crypto projects. And since BSC can offer all kinds of projects, from regular cryptocurrencies to NFT’s, from yield farming to play-to-earn games, it won’t be a problem to find a suitable project.
Still, just like any other blockchain, BSC has its own drawbacks, so keeping them in mind and matching them with your goals for BSC usage would be a wise idea.
FAQ
What consensus does BSC use?
The BSC consensus protocol is somewhat non-trivial, as it utilizes both delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS) and Proof of Authority (PoA) mechanisms to achieve consensus within the network and maintain blockchain security.
Is BSC a fork of Ethereum?
Even though Binance Smart Chain is perceived as a unique blockchain with its own technologies and capabilities, it’s interesting to note that Binance developed its Binance Smart Chain by forking the Go Ethereum (Geth) client but made a few modifications to set it apart from Ethereum.