Let’s take a look at Cardano (ADA) – the decentralized network often called a third generation cryptocurrency because it was developed in response to the challenges encountered in Bitcoin and Ethereum.
What is Cardano?

Cardano (ADA) is a proof-of-stake decentralized network that was developed with the goal to allow blockchain programmers and entrepreneurs to solve scalability, interoperability, and sustainability issues of the previous blockchains, such as Bitcoin and Ethereum. In plain English, with its more sophisticated approach, the project is challenging two major blockchains’ slow transaction times, draconian energy use, and growing costs. That might be the reason why the Cardano network is known publicly as one of the so-called Ethereum killers.
Why is its native token called ADA? The name belonged to the 19th century mathematician Ada Lovelace, who is often regarded as the world’s first computer programmer. We’ll talk more about the ADA token in detail later on, so stay tuned.
Cardano’s first live version was released in 2017. It has got a powerful infrastructure of organizations helping its commercial, social, and mainstream adoption. Cardano Foundation is an independent Swiss-based non-profit that oversees and supervises the advancement of Cardano. The IOHK research institute (also called sometimes Input Output Hong Kong) mostly engages in the academic incentives and studies of fintech blockchain infrastructure, and Emurgo is the official commercial and venture arm of the Cardano project registered in Tokyo.
Many white papers were produced over the past seven years by the IOHK research institute for public, private sector and government clients. However, Cardano has always been the institute’s main focus. Multiple scholars contributed to the enhancement of the blockchain’s ecosystem, and that slowly transformed into the project’s thing. Academics, professors and experts in the fields of gaming systems, computer programming languages, network design and cryptography have given a boost to Cardano development. And such an approach is a feather in the CEO’s hat, which he understandably likes to bring up.
Cardano’s history
As a project, the Cardano network was launched in 2015 by Charles Hoskinson, the Ethereum co-founder. However Hoskinson left Ethereum after getting into a tangle with Vitalik Buterin for the reason as old as this world – money. It is rumored that Buterin removed Hoskinson from Ethereum over a dispute of whether the project should be commercial (Hoskinson’s side) or a nonprofit (Buterin’s side). Ironically, Buterin now is one of the richest people in the blockchain niche with the estimated net worth approaching approximately $1 billion.
After the dispute with Vitalik, Charles Hoskinson, in his own words, was “pretty pissed off”. At a certain moment, Ether (ETH) started to approach a market capitalization of $120 billion. So Hoskinson decided to develop a blockchain project of his own, which could grow into something better and bigger than the Ethereum blockchain. He started working on Cardano in 2015. And when his former Ethereum colleague, Jeremy Wood, approached him, they formed IOHK, where Cardano was enhanced.
IOHK was the first organization they’ve created, later they’ve also launched Cardano Foundation and Emurgo.
On Jan 1, 2018, the Cardano Foundation closed its last funding round as a part of ICO, raising $62.2 million in total. Three known investors have participated, including MKT, James Sowers, and Julian Sarokin.
MKT is a venture firm you really don’t know much about. To date, Crunchbase lists only two investments that MKT has made. Interestingly, the first of these two investments was made in 2014 – in Ethereum.
James Sowers is a much more public figure in this sense. He has made 83 investments. And his latest investment was in ICO of Yield Guild Games on Jul 28, 2021, when Yield Guild Games raised $12.5M.
Julian Sarokin is also a private investor with 10 known projects in his portfolio, and his most prominent investment so far has been Ocean Protocol that raised a total of $22.1M.
With its 800k followers on Twitter and 50k followers on Telegram, the Cardano network is being supported by such board members as Jillian MacNab, a former Goldman Sachs executive director, and Andreas Eschbach, a former PwC partner. A business mentor Frederik Gregaard is also on the list of the team members of the project.
Cardano’s roadmap
Quite vivid and eye-catching, Cardano’s roadmap with pixelated pics of the legendary figures from the past represents different technological eras in the project development. In total, there are five stages of Cardano development: Byron, Shelley, Goguen, Basho, and Voltaire.
Let’s take a quick look at each of these stages.
- Byron (launched September, 2017) – the first incarnation of Cardano ecosystem that allowed users to buy and sell ADA. As the project’s website states, it was about the first crucial developments, as well as about building a community and getting users involved in supporting their blockchain technology.
- Shelley (launched July, 2020) – the era where more nodes run by the Cardano community were added. By the end of the Shelley era, Cardano became more decentralized. It allowed node operators to add their nodes to the network and allowed users to delegate their ADA to the staking pools.
- Goguen – (launched September, 2021, current era): with the Alonzo hard fork in 2021, this era introduced the community to smart contract capabilities. This was somewhat revolutionary for Cardano since it allowed users to create dApps in the network’s ecosystem.
- Basho (live sometime in 2022) – the period of optimization as well as scalability and interoperability. When the development progress matches this watershed mark, the sidechains will be introduced, which is, in fact, a sharding mechanism meant to off-load work from the main chain onto a sidechain.
- Voltaire (no release date yet) – the period where developers will add a voting and treasury functionality for the users to perform governance. Also, users will be able to stake their funds and earn rewards.
Cardano’s blockchain current architecture
Since we’re currently witnessing the Goguen era, and the Alonzo hard fork has already happened, the present-day state of Cardano blockchain technology consists of two layers. The first layer is Cardano settlement layer keeping track of ADA transactions. The second layer, Cardano computational layer, is enabling smart contracts and applications to run on the platform.
The first layer brings a throughput of 250 TPS (transactions per second). It’s more transactions than Bitcoin or Ethereum can process, since the next-generation Proof-of-Stake (PoS) consensus generates new blocks and confirms transactions faster than the old-generation Proof-of-Work (PoW).
The second layer, so to speak, operates from a separate box, closing computational gaps and making smart contracts run seamlessly. If anything happens, the other layer will stay intact.
Such a two-layer, proprietary implementation is basically a pot-shot taken at Ethereum with its single-layer architecture, representing congestion, slower transaction speeds, and higher fees.
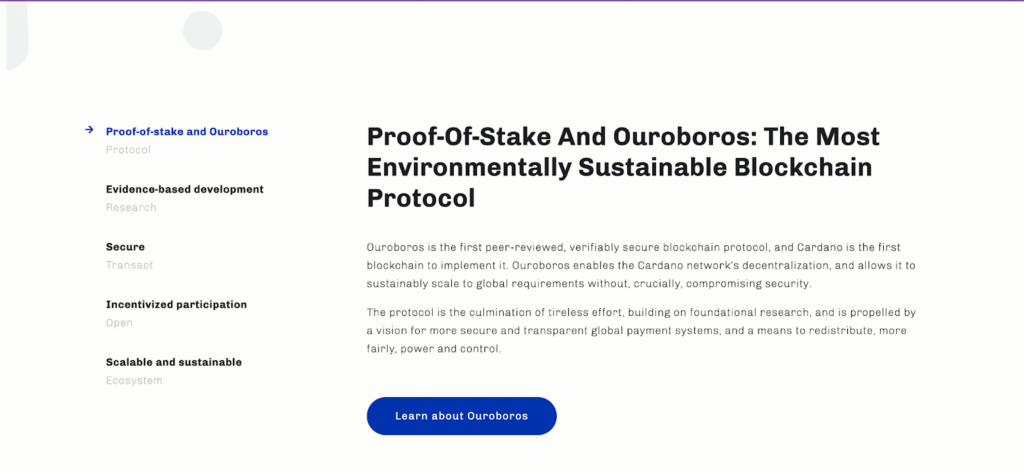
It’s also important to make a special mention of Cardano’s Ouroboros protocol, the enhanced version of Proof-of-Stake. According to the Cardano’s website, with Ouroboros, rather than relying on miners to solve computationally complex equations to create new blocks – and rewarding the first to do so – Proof-of-Stake selects participants (in the case of Cardano, stake pools) to create new blocks based on the stake they control in the network.
It’s also interesting to note that Ouroboros divides its blockchain network into slots and epochs. In Cardano, each slot lasts for 20 seconds and each epoch – which is an aggregation of slots – represents approximately five days’ worth of slots. A slot leader is elected for each slot, who is responsible for adding a block to the chain and passing it to the next slot leader.
What differentiates the Ouroboros consensus mechanism from any other blockchain technology, and, specifically, proof-of-stake protocols, is its ability to generate unbiased randomness in the protocol’s leader selection algorithm.
Cardano’s PoS blockchain characteristics
Let’s take a look at the three components that the Cardano team has proclaimed the most important for the project during their Byron (1st) era: scalability, interoperability, and sustainability.
Scalability
Definition: Scalability in blockchain networks is the ability of the decentralized network to process a large number of transactions in a short span of time. It is related to the block sizes of the blockchain network and to the frequency with which blocks appear on the network.
Talking about scalability, currently Cardano can process about 250 transactions per second (TPS). And the project’s developers are already working on a scaling solution that can provide the throughput of 1,000 TPS.
By comparison, this is more than Bitcoin’s five transactions per second, Ethereum’s 15 TPS and is the same as Polkadot’s 1,000 TPS. However, it’s less than Algorand’s 1300 TPS, 25,000 Fantom TPS, and Solana’s 50,000 TPS.
Interoperability
Definition: Interoperability is the ability to see, access, and share information across different blockchains or blockchain networks. Using so-called sidechains, bridges and swaps, and oracles, different blockchains communicate with one another. That enables you, as a user, or a business developer, or a programmer, to transfer tokens, and initiate actions across multiple networks.
Cardano has recently partnered up with Wanchain, thus, adding more than 15 networks to its ecosystem. Wanchain offers decentralized bridges connecting blockchain protocols with each other, which means that now such dApps on Cardano can be developed where you can use not only ADA. Now such coins as BTC, ETH, DOT, WAN, and XRP can be used for dApp development.
Does this development, however, make Cardano stand out among other blockchains? Over 20 blockchains, including Terra, Osmosis, Crypto.Org and Terra are now connected in the Cosmos ecosystem by the Inter-Blockchain Communication (IBC) protocol. Polkadot supports up to 100 parachains, with 17 live parachains where Acala and Moonbeam are the ones you’ve maybe heard of. And last but not least, Harmony currently offers bridges to 5 chains, including Ethereum and Bitcoin. In that sense, Cardano and its competitors run toward the brighter future neck to neck.
Sustainability
Definition: A sustainable blockchain is one with low energy consumption and minimal carbon footprint.
In terms of sustainability, Cardano’s founder, Charles Hoskinson, claims that the network consumes 6 GWh annually, compared to 17.49 GWh used by the Bitcoin network as estimated by the University of Cambridge. Talking about other blockchains, Polkadot is estimated to consume 0.8 GWh per year, and Ethereum – 300,000 GWh. Indeed, the latter is a catastrophic number, but when Ethereum shifts to the PoS era it should all be forgotten.
ADA price analysis and prediction for 2022-2025
Cardano’s native token, ADA, costs $0.5559 as of May, 16, 2022, bringing its market capitalization mark up to $15 billion.
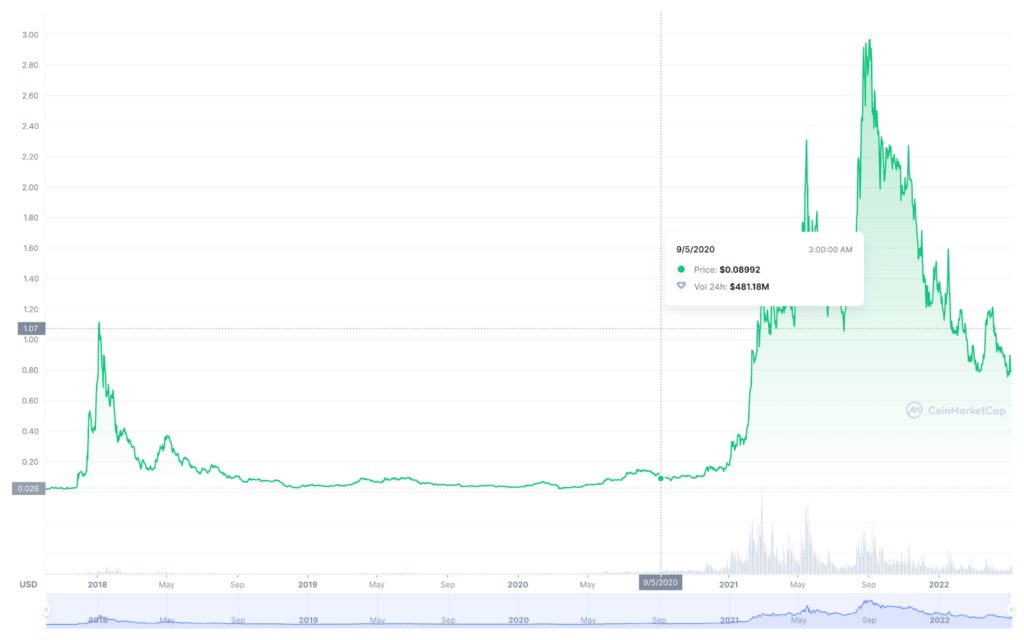
The platform has grown significantly over the past couple of years, with ADA token ranked the seventh-largest digital asset by market capitalization worldwide as of the same date. The Alonzo hard fork caused Cardano to gain 116% in the summer of 2021. Since then, ADA’ has been slowly going through a price correction, reigniting debates on whether Cardano is dead.
According to the Analytics Insight, the price of the asset in 2024 will be at $2.29 and record the growth of 147% from today. In 2025, Cardano will trade at a minimum of $3.68 and a maximum of $4.38. The average price is estimated to be $3.81.
If you want to exchange $ADA safely and anonymously, try Exolix – an instant cryptocurrencies exchange service with fixed and floating rates, which is free of registration and any limits. It features a user-friendly interface, a fast exchange process, and reliable 24/7 support.
So, with Exolix you can swap 490+ cryptocurrencies to $ADA and vice versa just in a few simple steps
Summing up
So, is Cardano breaking the barriers to blockchain scalability? However banal and generic that might sound, just like its competitors in the niche, it is not that one and only killer app (not that there should really be one). It doesn’t outperform every other blockchain project on all fronts, but it is a solid and established project with dedicated users, a proven team behind it and must-have characteristics nowadays – such as Proof-of-Stake, and a smart contract functionality. Cardano aims to solve scalability, interoperability, sustainability issues, and has $62 million in investment. In terms of technologies used, it definitely contrasts to any first generation cryptocurrency, promising a brighter future for the blockchain industry.
If the ambitious goals on the Cardano roadmap are completed earlier than their competitors’ equally ambitious goals, then, the project has a good potential for investment. But who can tell you for sure what will happen in the future? Be careful while building your prognosis on other people’s opinions expressed and do your own research before investing! Cryptocurrency markets are highly volatile and your investments are at risk.
Interested in investing in ADA? It is available on any prominent decentralized exchange, say Binance, HitBTC, Huobi, Bybit, Coinbase Pro and all the other major platforms. If you want not only invest but also trade the coin, taking advantage of the crypto market volatility without manual hassle of the trading routine – buy and sell easily, using automation tools and robots like TradeSanta. Still have questions? Shoot them on Facebook, Telegram, or Twitter!
FAQ
What is Cardano?
Cardano (ADA) is a proof-of-stake decentralized network that was developed with the goal to allow blockchain programmers and entrepreneurs to solve scalability, interoperability, and sustainability issues of the previous blockchains, such as Bitcoin and Ethereum.
